As you known, I’ve moved from HostGator to DigitalOcean for two months and I shared some tips to build your own perfect LAMP server optimize for WordPress. With the VPS expansion you can now get a (very) small virtual private server (VPS) for a very affordable price. However, when you get a server with something like 256MB or 512MB RAM and a portion of CPU power, using default MySQL/PHP/Apache settings is a pretty bad idea. Currently, I’m running 3 websites with DigitalOcean‘s lowest plan: 512MB RAM/1 CPU. Not sure for load, but lets say 5-10k visitors per day.
If you follow my guidelines in previous post, RAM usage will be increase up to 400 MB then running out in 1 – 2 weeks even you turned on swap. How to minimize memory usage on LAMP to prevent your server crash?
I’ve setup a working VPS Ubuntu 12.04 LTS, LAMP server in 512MB of memory and it hasn’t gone into swap yet. It typically runs in just over 256 – 378Mb of memory and performs really well. So I thought I’d share the process of setting it up.
How am I build perfect VPS with low RAM/CPU for Hight-Traffic WordPress websites
[digitalocean]
Determining Free Memory and Swap Activity
Before start optimizing your server, let’s review memory using on it. You can use the following command to display memory:
$ free -m
To see a list of your running processes sorted by memory use:
$ ps -eo pmem,pcpu,rss,vsize,args | sort -k 1 -r | less
Setup LAMP Server in a Low Memory Situation
Stop, Disable unused services
The first and obvious question to ask was what services do I not need? I recently discovered sysv-rc-conf that actually manages to nail the simplistic service management paradigm I was really looking for – by using freaking checkboxes:
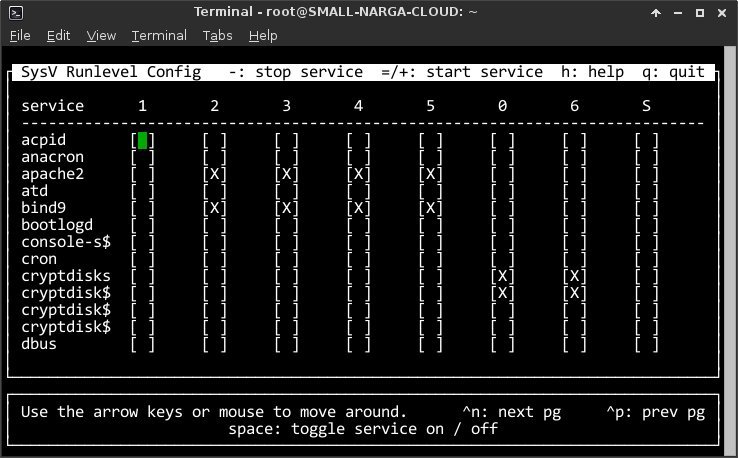
Here is list of services which I’ve changed:
- Postfix: This service let you sending & receiving email to your domain. I’m using Google Apps for emails and Mailchimp to manage newsletter’s subscribers. So I stop and disable Postfix server.
- Bind9: You can manage domain record with bind9 service, it’s stoped & disabled since I used Digital Ocean DNS services.
- SSHD: There are other implementations of sshd that use less memory, however the ones I considered did not support sftp and I need that, so I’m sticking with the standard install.
Don’t run X, shutdown all unneccesary services, and compile Apache, MySQL, and PHP with only essential functionality.
Apache
The biggest problem with Apache is the amount of ram is uses. I’ll discuss the following techniques for speeding up Apache and lowering the ram used.
- Handle Fewer Simultaneous Requests
- Loading Fewer Modules
- Log less
Tune Apache to only have a small number of spare children running.
Prefork is where the real magic happens. This is where we can tell apache to only generate so many processes. The defaults here are high it’s eating your server memory. Make your sure apache2.conf is not configured to start too many servers, or have to many spare server best weight loss sitting around. Reference the example below:
StartServers 1
MinSpareServers 1
MaxSpareServers 3
MaxClients 10
MaxRequestsPerChild 3000
StartServers 1
MinSpareThreads 5
MaxSpareThreads 15
ThreadLimit 25
ThreadsPerChild 5
MaxClients 25
MaxRequestsPerChild 200
Also, make sure to adjust KeepAliveTimeout to 10 or 15. In my opinion, 15 seconds is longer than a short page view requires, and shorter than a long page view requires.
Only load the modules you require
The default configuration file for apache also frequently loads every module it can. This is an especially big deal with the prefork mpm, as each apache instance will eat up geometrically more memory when unneeded modules are enabled. To check which apache modules are enabled/installed, use command below:
# apache2ctl -M
Default Apache modules (may be difference with yours):
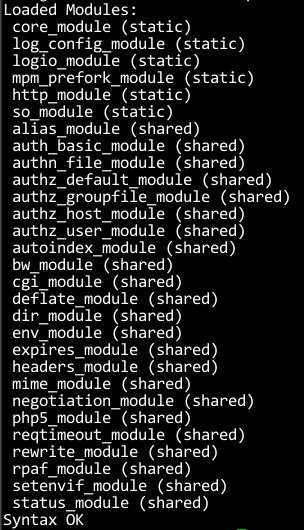
Here is list of Apache Modules which must be enabled for running WordPress:
LoadModule dir_module modules/mod_dir.so
LoadModule log_config_module modules/mod_log_config.so
LoadModule mime_module modules/mod_mime.so
LoadModule setenvif_module modules/mod_setenvif.so
LoadModule alias_module modules/mod_alias.so
LoadModule authz_host_module modules/mod_authz_host.so
LoadModule rewrite_module modules/mod_rewrite.so
Comment out any modules that aren’t needed to save yourself some more memory. Or you can change it by use commands below:
To enable a module:
# a2enmod module_name
To disable a module:
# a2dismod module_name
You must restart the server after enable/disable the modules:
# service apache2 restart
Log Less
If you’re trying to maximize performance, you can definitely log less. In my server, I set it to error lever. Also, if you don’t care about looking at certain statistics, you can choose to not log certain things, like the User-Agent or the http-referer.
# ErrorLog: The location of the error log file.
# If you do not specify an ErrorLog directive within a
# container, error messages relating to that virtual host will be
# logged here. If you *do* define an error logfile for a
# container, that host's errors will be logged there and not here.
#
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
#
# LogLevel: Control the number of messages logged to the error_log.
# Possible values include: debug, info, notice, warn, error, crit,
# alert, emerg.
#
LogLevel error
I like seeing those things, but it’s up to you.
Optimize MySQL server
Tweaking MySQL to use small amounts of memory is fairly straightforward. I’m going to try to show you the why instead of the what, so you can hopefully tweak things for your specific server. We’ll look at the following MySQL types of mysql settings:
- Things We Can Disable
- Turning MySQL Server Parameters
- Third Party Configuration Wizard for MySQL
To optimize mySQL we need to edit the mySQL configuration file, it’s /etc/mysql/my.conf
Things We Can Disable
MySQL allows a few different storage engines for its tables. The two most common are InnoDB and MyISAM. The main difference between the two is:
- MyISAM offers table-level locking, meaning that when data is being written into a table, the whole table is locked, and if there are other writes that must be performed at the same time on the same table, they will have to wait until the first one has finished writing data.
- InnoDB, on the other hand, offers row-level locking, meaning that when data is being written to a row, only that particular row is locked; the rest of the table is available for writing.
The problems of table-level locking are only noticeable on very busy servers. For the typical website scenario, usually MyISAM offers better performance at a lower server cost.
If you decide to use only MyISAM tables, you must add the following configuration lines to your my.cnf file:
default-storage-engine=MyISAM
default-tmp-storage-engine=MyISAM
If you only have MyISAM tables, you can disable the InnoDB engine, which will save you RAM, by adding the following line to your my.cnf file:
skip-innodb
If you use InnoDB from the past, here is a simple shell script to automatically convert InnoDB tables to MyISAM.
#!/bin/bash
MYSQLCMD=mysql
for db in `echo show databases | $MYSQLCMD | grep -v Database`; do
for table in `echo show tables | $MYSQLCMD $db | grep -v Tables_in_`; do
TABLE_TYPE=`echo show create table $table | $MYSQLCMD $db | sed -e's/.*ENGINE=\([[:alnum:]\]\+\)[[:space:]].*/\1/'|grep -v 'Create Table'`
if [ $TABLE_TYPE = "InnoDB" ] ; then
mysqldump $db $table > $db.$table.sql
echo "ALTER TABLE $table ENGINE = MyISAM" | $MYSQLCMD $db
fi
done
done
Turning MySQL Server Parameters
There are several parameters that can be adjusted on a MySQL server to make it faster.
Key buffer size
This is probably the single most important thing you can tweak to influence MySQL memory usage and performance. MySQL tries to put everything that’s indexed into the key buffer so this is a huge performance speedup. The SQL query will be served directly from RAM. I can’t say what size you should make your key buffer, because only you know how much ram you have free.
The Query Cache
If you do the same query two times in a row, and the result fits in the query cache, mysql doesn’t have to do the query again. If you’re going for performance, this can be a huge benefit, but it can also eat up memory. So, you need setting it’s not too high and low as your website needed.
There are three variables that influence how the query cache works.
- query_cache_size
- query_cache_limit
- query_cache_type
Maximum Number of Connections
It’s option parameter. If you’re already limiting the number of apache processes, then you’ll be fine. If you’re not, and you need to handle thousands of users simultaneously, you need to increase this number.
The Table Cache
Every time you access a table, MySQL loads a reference to a table as one entry in the table cache. This is done for every concurrent access of a table, it’s really important for performance, marginally so for memory usage. You can keep upping the table cache, but you’ll eventually hit a limit on the number of files your operating system can have open, so keep that in mind. If table cache is set too low, mysql will barf on you, and you don’t want that.
Here is current my.conf that I’ve optimized on my VPS with lowest Digital Ocean plan.
[mysqld]
port = 3306
socket = /var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
skip-locking
key_buffer = 16K
max_allowed_packet = 1M
table_cache = 4
sort_buffer_size = 64K
read_buffer_size = 256K
read_rnd_buffer_size = 256K
net_buffer_length = 2K
thread_stack = 64K
# For low memory, InnoDB should not be used so keep skip-innodb uncommented unless required
skip-innodb
# Uncomment the following if you are using InnoDB tables
#innodb_data_home_dir = /var/lib/mysql/
#innodb_data_file_path = ibdata1:10M:autoextend
#innodb_log_group_home_dir = /var/lib/mysql/
#innodb_log_arch_dir = /var/lib/mysql/
# You can set .._buffer_pool_size up to 50 - 80 %
# of RAM but beware of setting memory usage too high
#innodb_buffer_pool_size = 16M
#innodb_additional_mem_pool_size = 2M
# Set .._log_file_size to 25 % of buffer pool size
#innodb_log_file_size = 5M
#innodb_log_buffer_size = 8M
#innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit = 1
#innodb_lock_wait_timeout = 50
[mysqldump]
quick
max_allowed_packet = 16M
[mysql]
no-auto-rehash
# Remove the next comment character if you are not familiar with SQL
#safe-updates
[isamchk]
key_buffer = 8M
sort_buffer_size = 8M
[myisamchk]
key_buffer = 8M
sort_buffer_size = 8M
[mysqlhotcopy]
interactive-timeout
Third Party Configuration Wizard for MySQL
I’ve found Percona provide a free Configuration Wizard for MySQL that help you choose the best features of MySQL server to achieve better MySQL database performance and avoid the time, complexity, and risk of customizing a my.cnf configuration on your own.
MySQL Server Monitor
MySQL stores statistics that will help you to determine the best values that you must use. Furthermore, there are two handy utilities that can be used to read these statistics and print them on an easy-to-understand format: tuning-primer.sh and mysqltuner.pl.
These scripts will monitoring your MySQL server, at the end of its report, give you a hint of the parameters you should adjust on your server.
Optimize PHP & Caching
PHP is not very memory intensive, so I don’t think you should worry too much about memory usage, unless your app needs it, in which case the memory footprint of PHP won’t be too significant. But I’ve researched then found some tweaks of PHP configuration that decrease memory usage of your webserver.
; Limit the memory to 40M should be fine for barebones WordPress
memory_limit = 48M
realpath_cache_ttl=300
realpath_cache_size=1M
Alternative PHP Cache
Install a PHP Cache such as Alternative PHP Cache. The PHP cache will store compiled PHP scripts so that they can be reused without the overhead of compiling and processing them for each request.
# pecl install apc
And my php.ini configuration
[APC]
extension=apc.so
apc.enabled=1
apc.shm_segments=1
;32M per WordPress install
apc.shm_size=128M
;Relative to the number of cached files (you may need to watch your stats for a day or two to find out a good number)
apc.num_files_hint=7000
;Relative to the size of WordPress
apc.user_entries_hint=4096
;The number of seconds a cache entry is allowed to idle in a slot before APC dumps the cache
apc.ttl=7200
apc.user_ttl=7200
apc.gc_ttl=3600
;Setting this to 0 will give you the best performance, as APC will
;not have to check the IO for changes. However, you must clear
;the APC cache to recompile already cached files. If you are still
;developing, updating your site daily in WP-ADMIN, and running W3TC
;set this to 1
apc.stat=1
;This MUST be 0, WP can have errors otherwise!
apc.include_once_override=0
;Only set to 1 while debugging
apc.enable_cli=0
;Allow 2 seconds after a file is created before it is cached to prevent users from seeing half-written/weird pages
apc.file_update_protection=2
;Leave at 2M or lower. WordPress does't have any file sizes close to 2M
apc.max_file_size=2M
;Ignore files
apc.filters = "/var/www/apc.php"
apc.cache_by_default=1
apc.use_request_time=1
apc.slam_defense=0
apc.mmap_file_mask=/var/www/temp/apc.XXXXXX
apc.stat_ctime=0
apc.canonicalize=1
apc.write_lock=1
apc.report_autofilter=0
apc.rfc1867=0
apc.rfc1867_prefix =upload_
apc.rfc1867_name=APC_UPLOAD_PROGRESS
apc.rfc1867_freq=0
apc.rfc1867_ttl=3600
apc.lazy_classes=0
apc.lazy_functions=0
Static Cache
Another thing that could be a great idea for a blog on a small server is to put it behind a static-HTTP-cache like Varnish. That can really boost your scalability. Configuring Varnish is a complex and large topic that requires its own blog post, however.
Conclusion
I’ve shared my webserver configuration to get best perfomance with lowest Digital Ocean’s droplet: 512MB RAM/1 CPU. I’m using Ubuntu 12.04 LTS, LAMP, Varnish, APC Cache to hosting 3 WordPress website (not Multisite) and alive with 10k visitors per day. Let’s see the Blitz.io test result:
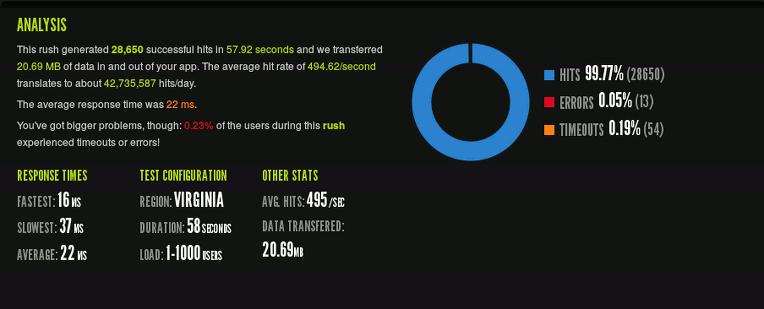
As you see, 0.23% of the users got Connection Timeout when my website has 42,735,587 hits/day (WoW), may I have somethings to do but I’m feel pleasure with my server.
If you feel tired with this guide or don’t want do it by hands, let’s try PuPHPet or Vagrant
Thanks for the guide. Simple enough for a newbie like me, but I’m still using a lot of RAM without any traffic on my wordpress site. Are you hosting this site (Narga) on a VPS with these settings?
Do you have any more tips for optimizing Ubuntu in general? Not just Apache/PHP/MySQL.
Yes, I’m running 5 website (3 WordPress, 1 AnchorCMS, 1 PHP gallery, 1 static website) with lowest plan. It’s recevied 6-10k pageviews per day. Currently I use LAMP (ZPanel), Varnish, PHP Memcache. The maximium process of Apache are 3 process, MySQL server with smallest configuration.
The biggest proccess that uses most server resource is Varnish, it’s cost my server about 18.6% MEM and 1.2% CPU.
Everything was cached.
Are your turned on the swap? Have you re-config apache to get lowest wordkers?
Hmmm I will have to check out those caches (or what about wordpress cache plugins?). But my site has no traffic yet, just testing, so I don’t know how much caching will help.
I don’t have swap turned on. I heard it’s not good on a VPS. I did configure Apache and it saved a little more RAM. I might need to disable some more Apache modules.
Thanks anyway.
The swap don’t turn on if you running a high RAM VPS.
Have you check your memory usage with
Are you optimize MySQL service to decrease the memory usage?
Nice tips, i can sure use some of these.
I have one wordpress running on a 512MB droplet too.
With LAMP and for some reason my MySQL server was constantly stopping, so i was getting “fail to connect to database” almost everyday. So i search in the web for solutions and ended up removing apache and using ngnix and since them everything is working fine.
Now with the tips that you posted i guess i wont have any problems in the future since i don’t even get half of those daily hits.
You got
fail to connect to databasemessage because the MySQL process was killed because out of memory. You need turn on the swap then optimize apache, mysql configuration to decrease the memory usage.If your Apache configuration optimized, it works better than Nginx :D
Currently, I’m running 5 website on lowest droplet with 512MB RAM, 1 CPU, about 6-10k pageviews per days and has 8% RAM + 60% Swap free.
Seems you have moved to Nginx? why?
I moved to Nginx because its low memory footprint and I can host 5 WP sites on lowest VPS plan
Impressive. I had trouble with the lowest plan but I was looking for these performance tweak. Something I should definitely test, can save a money with this!
Nice – I’ll try some of these things even though I’m running a LEMP server, not Apache. Currently
/usr/sbin/mysqldis using the most Memory/Virtual Memory on my server.My droplet says it’s using 44% of memory but then when I look using
ps -eo pmem,pcpu,rss,vsize,args | sort -k 1 -r | lessit shows maybe 10% of actual memory being used and VSZ is looking large (though I’m not sure)./usr/sbin/mysqldis using 327364 Vsize… is that a lot?Also wanted to point out that, at least for me, it’s
/etc/mysql/my.cnfnot/etc/mysql/my.confYes, LEMP is better than LAMP if it has optimized but you will find some problem with .htaccess, scripts … because it’s wrote for Apache only.
I’m not find the way to view droplet’s memory usage from DO CP but I think the result of system command is correctly.
My file
/etc/mysql/my.confbecause I’m using Arch Linux, if you use Ubuntu it’s called as/etc/mysql/my.cnf:DHi
Thanks for your great article. I have optimized as you suggested. At the end I did blitz testing and I am facing issues.
Initially I got lot of 502 error when I checked my error logs in nginx. so i found out that through this post about the issue that its common if you are not using TCP port for php :
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/10470109/error-502-in-nginx-php5-fpm
so now I used TCP port for php-fpm but now I am getting timeouts saying “worker_connections are not enough while connecting to upstream”
Could you tell me how you achieved such great blitz result in your droplet. What settings are you using in nginx and php.
Thanks. Looking forward to your reply.
Oh, current time I’m using Apache, MySQL… not Nginx so I can’t share it for you.
Just wait, I’m changing to Nginx then I will writing about it in future, just testing it before move everything to next server software.
Sure. I will be looking forward to your nginx setup article.
In the last line of this article you mentioned a link to PuPHPet and Vagrant. It would have been nice to include a configuration file similar to yours for use with these services. I am on one of those 512MB plans with DO and i keep getting database connection errors with my site (with 1 visitor, me).
What you have done with your configuration is almost magical. Honestly. I have been struggling to fix this issue, i gave up and switched to Nginx. The problem is gone but i fear it my return with more load.
How about writing a ‘How-to’ articles with step by step instructions and terminal commands? That would be so helpful. This MySQL errors are VERY common with DO’s 512 vps solutions and you would help ALOT of people.
As I mentioned above. I’m using DO with lowest plan like you: 1 CPU, 512MB RAM, Ubuntu 12.04. It’s running 3 sites and has about 10k visitors per day but last boot time of that droplet from 5 months ago. That is unbelievable but it’s true.
I agree with you that MySQL is most problem and it’s eating too much memory but you can control it with my suggest configuration above. Let’s trying it with step by step, don’t copy and past whole file content.
Are you using Ubuntu 12.4 or later version? May be it’s one cause of your problems.
@ Đình Quân Nguyễn… Thank for you response.
Right now i am in the experimenting stage, getting familiar with managing my own server. As such i am researching and trying out many things, one of the experiments lead me to Nginx. I moved from Apache to Nginx and the problem is gone. I also did a Blitz.io rush the it held up well.
After that i did ‘easygine’ and there setup also ran pretty well. Tomorrow i an trying ‘centminmod’. My sites are still on a shared hosting account so i have time to play around some more.
BTW i am glad i found your article, it lets me know what i can expect from a similiar setup
Hi,
first of all, thanks for your article. I spent several days fighting with my Apache & MySQL because it died frequently, so I found your post very useful.
I only want to add a link to an article on Digital Oceans about how to configure Varnish (between others): https://www.digitalocean.com/community/articles/how-to-install-wordpress-nginx-php-and-varnish-on-ubuntu-12-04
Currently I’m using Apache because as you told, .htaccess is only for it, but I want to try to use wordpress with nginx as a challenge, maybe in another cheap-droplet :)
The guide to configure Varnish on that article just give you a small effect with default variables of Varnish. But it works on most droplet :)
So, and disabling Postfix without providing something alternative (msmtp) will make the system silent, very silent. Even system mails (e.g. cron) won’t make it everywhere. Maybe not a good idea. ;)
If you don’t want send email to others or use alternative mailing list services like MailChimp, …
You had a good idea :D
StartServers 1 MinSpareServers 1 MaxSpareServers 3 MaxClients 10 MaxRequestsPerChild 3000 StartServers 1 MinSpareThreads 5 MaxSpareThreads 15 ThreadLimit 25 ThreadsPerChild 5 MaxClients 25 MaxRequestsPerChild 200I’m using your settings, but it hangs the server if there are more than 7 users simultaneously, what happen?
Have you use only pure LAMP or installed Hosting Control Panel like ZPanel or similar? If your Apache still increases the workers, it might control by other software.
wow, what a cool post
i tried to do the tutorial, and i got a nice result
would you tell me how to configure varnish for this tutorial?
i am using a 1024MB digitalocean droplet + zpanel 10.1.1 + 3 wordpress site
after installing varnish, i can’t open the ajaxplorer
then i try to install pydio
i can open pydio, but i can’t upload any files
but while varnish removed, the ajaxplorer can be opened normally and upload file to pydio
can you share the varnish configuration?
thanks
You need configurate your varnish to ignore pydio, for example:
### do not cache these files: ##never cache the admin pages, or the server-status page if (req.request == "GET" && req.request != "HEAD" && req.request != "PUT" && req.request != "POST" && req.request != "TRACE" && req.request != "OPTIONS" && req.request != "DELETE" && (req.url ~ "(wp-admin|bb-admin|server-status)")) { return(pipe); }thanks
i put these lines in varnish/default.vcl
sub vcl_recv { if (req.url ~ "^/etc/apps/ajaxplorer/index.php") { return (pass); } if (req.url ~ "^/pydio/") { return (pass); } if (req.url ~ "^/usr/share/pydio/") { return (pass); } if (req.url ~ "^/usr/lib/pydio/") { return (pass); } if (req.url ~ "^/etc/apps/phpmyadmin/") { return (pass); } }now i can open pydio and upload any files
but i can’t open archive file (zip) while using varnish
so does the ajaxplorer, i can open ajaxplorer, upload files, but can’t open any archived (zip) files
any suggestion?
Fantastic post! Thanks for the level of detail too!
Why not use Nginx instead of Apache? That would save even more RAM.
P.S. btw Russian translation of this article is here: http://habrahabr.ru/post/242011/
Thanks for translated my article to russian. After moved to Digital Ocean, I started with LAMP but it’s eating too much memory so I switched to LEMP then it’s working perfectly.
I’ve wrote some articles about LEMP installation and optimization, you can find it here or search for nginx keyword with Search Box on the topbar.
Hi,
with your configuration sometimes my site is down and in the apache log file I see this:
[Thu Jan 15 11:33:26 2015] [error] server reached MaxClients setting, consider raising the MaxClients setting
do you have a solution?
I have tha same server as you have.
Thank you so much great post.
OMG, this article has been published for a long time ago and I switched to Nginx.
To solve it, you can increase the MaxClient setting because your scripts need more CPU Usage to done its job.
Thanks for your answer, do you have a guide to migrate from Apache to Nginx? I am using wordpress. Thanks
nice article to keep the server sane. However do you have article removing apache and switch to Nginx? Looking forward to that
I write an article to show How can I run 10 websites on Digital Ocean’s lowest hardware with nginx
Hi, the inno_db_buffer_pool_size default is 8MB, do you recommend increasing this? I see some articles talking about incresing this to 64M. What do you recommend for less consuming?
Thanks!
I’m not recommend because I prefer optimize it on a small and low RAM VPS, I’ve used for my old VPS with just 512MB of memory. If you increase it to 64MB, you’ll facing the blank of death of WordPress :D
I am currently using opcache and I had already setup the MySQL to use much less memory.
Just by using the first part of the Apache section of the post I was able to drop my memory usage down from 55% to 30%. Thanks a bunch =)
I recommend nginx for better solution of small and medium server. Nice to know my configuration is helpful for you.
I have 5 virtual servers and have maximum 10-20 real-time users and max 4k daily visitors. And the user can only interact with the website just to comment, no other data can be entered by the user.
What would be the best configuration for it?
My existing file apache and mysql configurations are following.
StartServers 5
MinSpareServers 5
MaxSpareServers 10
ServerLimit 8
MaxClients 50
MaxRequestsPerChild 1000
StartServers 5
MaxClients 100
MinSpareThreads 1
MaxSpareThreads 4
ThreadsPerChild 25
MaxRequestsPerChild 0
And MySQL Config file is
[mysqld]
bind_address = 0.0.0.0
datadir=/var/lib/mysql
socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
user=mysql
thread_cache_size=4
join_buffer_size=4M
sort_buffer_size=4M
read_buffer_size=4M
read_rnd_buffer_size=6M
myisam_sort_buffer_size=32M
key_buffer_size=32M
tmp_table_size=32M
max_heap_table_size=64M
query_cache_size=64M
query_cache_type=1
default-storage-engine=myisam
#skip-innodb
[mysqld_safe]
log-error=/var/log/mysqld.log
pid-file=/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid
Please Help.
My resource configuration is –
Operating system CentOS Linux 6.9
Kernel and CPU Linux 2.6.32-042stab125.3 on x86_64
Virtual memory 500 MB total
Real memory 1000 MB total
Local disk space 40 GB total / 36.90 GB free
Can you tell me the values of variables according to my requirements??
Hello NARGA,
I have ram 4gb but not enough for around 4-5 website haha..
I’m a newbie and now trying to do with your suggestion.
Thanks